Have you ever made changes to your website’s DNS records and wondered, “how long does it take for DNS records to update?” Understanding the intricacies of DNS propagation time is crucial for developers and website administrators alike. In this blog post, we’ll explore the factors that impact DNS record update times, provide practical tips for speeding up the process, and answer some frequently asked questions about DNS propagation.
What is DNS Propagation?
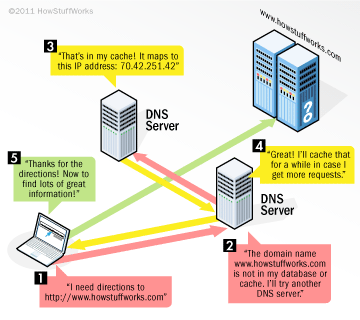
DNS (Domain Name System) propagation refers to the time it takes for DNS record changes to be recognized and updated across the global network of DNS servers. When you update a DNS record, it doesn’t immediately take effect everywhere. Instead, the updated information needs to propagate through the vast array of DNS servers worldwide, each of which caches DNS records for a certain period to minimize lookup times and reduce the load on the system.
Looking to enhance your development prowess? Find some great books here: Great books for developers
Factors Influencing DNS Propagation Time:
- Time To Live (TTL) Value: The TTL value of a DNS record determines how long it will be cached by a DNS server before it’s considered “stale” and needs to be refreshed. A lower TTL value will result in more frequent updates, but it may also increase the load on your DNS servers. Conversely, a higher TTL value reduces server load, but it can lead to longer propagation times when changes are made.
- DNS Server Cache: Each DNS server maintains its cache of DNS records. If a server has already cached a record, it may not immediately reflect the updated record until the cache expires, as determined by the TTL value.
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs): ISPs also maintain their DNS cache, which can cause additional delays in DNS record updates. The cache duration depends on the ISP’s policies and may vary significantly between different providers.
- Geographic Location: The geographic location of the DNS server requesting the updated record can impact propagation time. The further away a server is from the authoritative DNS server, the longer it may take for the update to be recognized.
Tips to Speed Up DNS Propagation Time:
- Set Appropriate TTL Values: Adjust your DNS records’ TTL values to balance the need for frequent updates with the potential impact on server load. Consider using a lower TTL value for records that may require more frequent changes, while keeping a higher TTL for more stable records.
- Flush Local DNS Cache: If you ‘re experiencing delays in DNS propagation, try flushing your local DNS cache. This may help to clear out old records and ensure that your device retrieves the most up-to-date information.
- Use a Global DNS Checker: To verify whether your DNS changes have propagated globally, use a global DNS checker tool. These tools can help you assess the status of your DNS records on various servers worldwide, giving you a clearer picture of the update’s progress. Check out this DNS Checker service for free
Conclusion:
While the time it takes for DNS records to update can vary depending on several factors, understanding the ins and outs of DNS propagation can help you make informed decisions about managing your website’s DNS records. By adjusting your TTL values, flushing your local DNS cache, and using global DNS checkers, you can reduce propagation time and ensure that your website’s updates are recognized quickly and efficiently across the internet.
Remember, DNS propagation time is not an exact science, and updates may take longer to propagate in some situations. However, by following these tips, you can minimize the impact of propagation time on your website’s functionality and improve your users’ experience.
If you’re still experiencing issues with DNS propagation or have any questions about managing your website’s DNS records, don’t hesitate to reach out to a professional web developer or IT specialist for assistance.
FAQs about DNS Propagation:
-
What is the average DNS propagation time?
The average DNS propagation time typically ranges from a few minutes to 48 hours. However, this time can vary depending on factors such as TTL values, DNS server cache, ISP cache policies, and geographic location.
-
Can I force DNS propagation to speed up?
You can’t force DNS propagation, but you can take steps to speed it up. Setting appropriate TTL values, flushing your local DNS cache, and using global DNS checkers are some ways to reduce propagation time.
-
Why do some DNS changes propagate faster than others?
The speed of DNS propagation can depend on the TTL value set for a particular record, the caching policies of DNS servers and ISPs, and the geographic location of the servers involved in the propagation process.
-
What happens if I make multiple DNS changes within a short period?
If you make multiple DNS changes within a short period, it’s possible that some changes may not propagate as quickly as others. This could be due to the cache settings on various servers and ISPs or the TTL values set for the individual records.
-
How do I know when my DNS changes have fully propagated?
To check if your DNS changes have fully propagated, you can use a global DNS checker tool, which will show you the status of your DNS records on servers worldwide.
-
Do all DNS servers update at the same time?
No, DNS servers do not update at the same time. Each server has its own caching policies and may refresh its cache at different intervals based on the TTL values of the DNS records.
-
Can DNS propagation cause website downtime?
In some cases, DNS propagation can cause temporary website downtime or inconsistencies. If the DNS records for your website are not updated consistently across all DNS servers, some users might still access your website using old records, while others might see the updated records. It’s essential to minimize downtime by planning your DNS changes carefully and implementing the tips mentioned above to speed up propagation.
-
What is the role of the TTL value in DNS propagation?
The TTL (Time To Live) value of a DNS record determines how long a DNS server caches the record before it is considered “stale” and needs to be refreshed. A lower TTL value results in more frequent updates but may increase the load on your DNS servers, while a higher TTL value reduces server load but may lead to longer propagation times when changes are made.
-
How can I verify if my DNS changes have propagated?
To verify if your DNS changes have propagated, use a global DNS checker tool that can help you assess the status of your DNS records on various servers worldwide.
-
Is there any way to bypass DNS propagation time?
While you can’t bypass DNS propagation time entirely, you can minimize its impact by setting appropriate TTL values, flushing your local DNS cache, and using global DNS checkers to monitor the progress of your DNS updates.
-
Why is my website still not accessible even after DNS propagation?
If your website remains inaccessible even after DNS propagation, there could be other issues at play, such as server misconfiguration, website coding errors, or issues with your hosting provider. In such cases, it’s essential to troubleshoot the problem by checking your server settings, reviewing your website’s code, or contacting your hosting provider for assistance.
By understanding the factors influencing DNS propagation time and following the tips provided in this article, you can ensure smoother DNS updates and minimize the impact of propagation time on your website’s functionality and user experience. If you continue to face challenges related to DNS propagation, consider reaching out to a professional web developer or IT specialist for support. For more information on other programming & development, check out our How To Guides.







